Net Present Value: How to Calculate NPV
For an individual that might mean, depositing your $100 in a high-yield savings account earning 5% interest rate, buying stocks or bonds, or some other investment like real estate or starting a business. The application of the formula depends on the number of expected cash flows for an investment or project. Investors use NPV to evaluate potential investment opportunities, such as stocks, bonds, or real estate, to determine which investments are likely to generate the highest returns. NPV is widely used in capital budgeting to evaluate the profitability of potential investments in long-term assets, such as machinery, equipment, and real estate. Both NPV and ROI (return on investment) are important, but they serve different purposes.
NPV Analysis in Excel (XNPV Function)
With stocks, for example, net present value can give you an idea of whether a company is a good buy or not by calculating NPV per share. Finally, it’s difficult to use net present value to evaluate projects or investments that are different in size or nature, as the input values are likely to be very different. Depending on whether you’re trying to target a specific dollar amount or percentage amount for returns, you may apply one or both formulas when evaluating an investment. • NPV is used in capital budgeting to assess the return on project investments before committing funds. Therefore, XNPV is a more practical measure of NPV, considering cash flows are usually generated at irregular intervals.
How confident are you in your long term financial plan?
- In corporate securities, NPV is often referred to as Discounted Cash Flow analysis.
- Once you add up all your present values of future cash, you need to compare that figure to the amount you’re thinking of investing.
- Net Present Value (NPV) is the value of all future cash flows (positive and negative) over the entire life of an investment discounted to the present.
- By looking at discounted cash flows you can get a better understanding of the viability of an investment, based on what you’ll get out of it versus what you’ll put in.
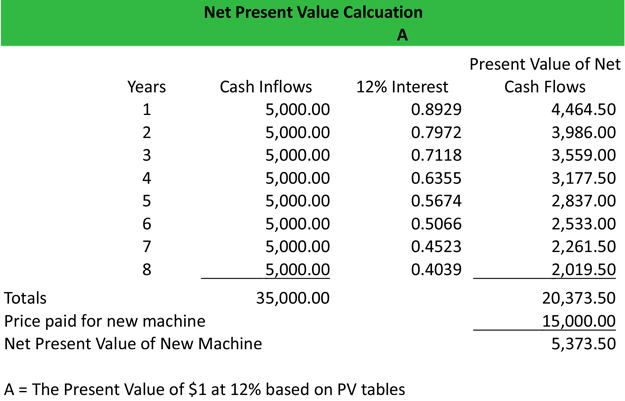
Weighted average cost of capital (WACC) usually serves as the discount rate for calculating NPV. The initial investment of the project in Year 0 amounts to $100m, while the cash flows generated by the project will begin at $20m in Year 1 and increase by $5m each year until Year 5. Although this is a great tool to use when making investment decisions, it’s not always accurate. Since the equation depends on so many estimates and assumptions, it is difficult to be completely accurate. Going back to our example, Bob has no idea that the interest rate will stay at 10 percent for the next 10 years.
How to Calculate NPV Using Excel
It is the discount rate at which the NPV of an investment or project equals zero. The reliability of NPV calculations is highly dependent on the accuracy of cash flow projections. Inaccurate projections can lead to misleading NPV results and suboptimal decision-making. A zero NPV implies that the investment or project will neither generate a net gain nor a net loss in value. In this situation, decision-makers should carefully weigh the risks and potential benefits of the investment or project before making a decision. For example, IRR could be used to compare the anticipated profitability of a three-year project with that of a 10-year project.
The discount rate is OFTEN based on a company’s weighted-average cost of capital (WACC… click HERE for the definition). The discount rate is a critical component of a discounted cash flow model (like NPV). In capital budgeting, calculating the net present value can help with estimating the profitability of an investment or expansion project. A discounted cash flow model takes the concept to time value of money and creates a model to tell you what those future cash flows are worth today.
How To Calculate?
A positive number means the future cash flows of the project are greater than the initial cost. If the number is negative, however, the company will spend more money purchasing the equipment than the equipment will generate over its useful life. As long as interest rates are positive, a dollar today is worth more than a dollar tomorrow because a dollar today can earn an extra day’s worth of interest. Even if future returns can be projected with certainty, they must be discounted because time must pass before they’re realized—the time during which a comparable sum could earn interest.
After the initiation of project, existing equipment with book value of $80,000 can be sold at $100,000. The hurdle rate applicable to the project is 12% and the company’s tax rate is 40%. Working capital of $130,000 is required at time 0 which shall be released at the end of the project. A company will often look to use a “cost of capital” or a “weighted-average cost of capital” (or WACC) as their discount rate.
As discussed, Net present value, or NPV, represents the difference between the present value of cash inflows and outflows over a set period of time. Understanding the net present value formula can help with making smarter investment decisions. Net present value’s main advantage is that it takes the time value of money into consideration. By looking at discounted cash flows you can get a better understanding of the viability of an investment, based on what you’ll get out of it versus what you’ll put in. Return on investment, or ROI, measures the efficiency of an investment, in terms of the rate of return that the investment is likely to produce.
Net Present Values for alternative investments can be used to directly compare their potential. The value of current cash inflows is known, certain and it has the potential to make a return. The initial investment outlay equals total initial investment in new equipment, test runs, etc. minus the after-tax proceeds of any equipment that can be disposed of or used for another project. We have first subtracted depreciation to find the net income and then multiplied by (1 – Tax Rate) to get the after-tax income and then added back depreciation to get net cash flows.
To illustrate the concept, the first five payments are displayed in the table below. A young professional decides to contribute to a retirement account, such as a 401(k) or an IRA. This investment decision involves evaluating contribution limits, tax advantages, and investment options within the account. The individual earned income tax credits in california considers their retirement goals and time horizon, deciding how much to invest regularly and which funds or assets to allocate within the retirement account to achieve growth over time. The payback period calculates how long it will take for the initial investment to be recovered from the project’s cash inflows.

